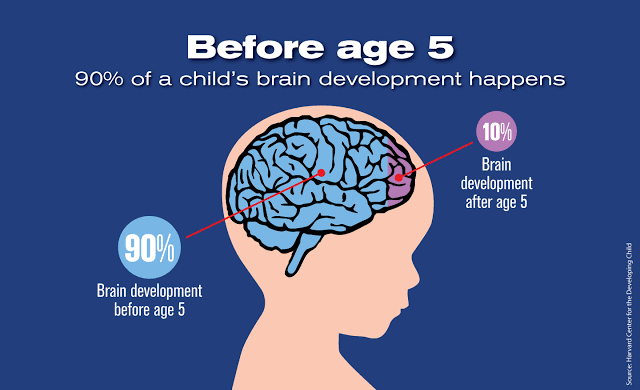
The potential of Early Childhood Education (ECE) to map an individual’s developmental course, setting the stage for continued learning, can hardly be overemphasized—in Nigeria, as in much of the rest of the world. States that invest in this sector get improved learning outcomes. Some of these outcomes are cognitive, social, emotional, and physical growth, the basic foundations of which are generally from the time of birth to around 8 years of age.
Current Status of Early Childhood Education in Nigeria
Nigeria, the most populace country in Africa, is faced with a number of problems on ECE. It is lamented that in spite of the efforts made by various organisations both governmental and nongovernmental, the access to quality ECE remains largely limited particularly in the rural and underserved parts, these are the problems of Inadequate infrastructure, Insufficient funding, Shortages of competent facilitators amongst others; which is contributing to the overall disparities in Early childhood education (ECE) provision across the country.
In towns such as Lagos, and Abuja, where private daycares and kindergartens serve families with high-paying jobs, the public schools have problems accommodating all the young learners they must. Additionally, in rural regions, neither decent preschool nor basic education services exist at all, and this is one significant source of educational inequality starting in the youngest years of school.
Early Childhood Education Yields Substantial Gains
Therefore, investing in Early Childhood Education results in enormous benefits that transcend the classroom. Research has established an overall pattern demonstrating the positive impact of high-quality ECE programs on children:
1. Improved Cognitive Development
Early learning activities, such as storytelling, interactive play, and educational games, stimulate brain development and enhance cognitive skills like problem-solving, critical thinking, and language proficiency. These foundational skills provide children with a robust academic base as they progress through formal schooling.
2. Enhanced Social and Emotional Skills
ECE fosters socialization and emotional regulation by encouraging collaboration, empathy, and conflict resolution among peers. Children learn to express their emotions, develop self-confidence, and build positive relationships, laying the groundwork for healthy social interactions in adulthood.
3. Better Academic Performance
Early exposure to literacy, numeracy, and basic concepts prepares children for academic success in primary school and beyond. ECE programs that focus on early literacy skills, such as phonics and vocabulary development, contribute to improved reading comprehension and overall academic achievement.
4. Long-term Health and Well-being
Early childhood education promotes healthy habits, including nutrition, physical activity, and hygiene practices, which are crucial for physical and mental well-being throughout life. Educators and caregivers play a vital role in promoting healthy behaviors and preventing childhood illnesses.
5. Reduction in Socioeconomic Disparities
Access to quality ECE can mitigate socioeconomic inequalities by providing disadvantaged children with the skills and opportunities needed to break the cycle of poverty. Early intervention programs that target at-risk populations contribute to equitable access to education and promote social mobility.
Challenges and Barriers
Despite the undeniable benefits, several challenges hinder the effective delivery of early childhood education in Nigeria:
Infrastructure and Resources:
Many ECE centers lack adequate infrastructure, including classrooms, play areas, and learning materials. Limited access to electricity, clean water, and sanitation facilities further compounds these challenges, particularly in rural communities.
Teacher Training and Professional Development:
The shortage of qualified early childhood educators remains a critical issue. Effective teaching in ECE requires specialized training in child development, curriculum planning, and instructional strategies tailored to young learners' needs.
Parental Awareness and Involvement:
Cultural beliefs, socioeconomic factors, and lack of awareness about the importance of ECE contribute to low enrollment rates and parental engagement. Addressing these barriers requires community outreach, parent education programs, and partnerships between schools and families.
Policy and Funding Constraints:
Inadequate government funding and inconsistent policies hinder efforts to expand access to quality ECE nationwide. Advocacy for increased investment in early childhood education is essential to prioritize children's rights to quality education and holistic development.
Strategies for Enhancing Early Childhood Education
To address these challenges and maximize the benefits of early childhood education in Nigeria, stakeholders must collaborate on comprehensive strategies:
1. Policy Reform and Advocacy
Advocating for policies that prioritize ECE funding, teacher training, and infrastructure development is crucial. Governments, NGOs, and civil society organizations can work together to influence policy decisions and allocate resources effectively.
2. Professional Development for Educators
Providing ongoing training and professional development opportunities for ECE teachers enhances teaching effectiveness and supports continuous improvement in curriculum delivery and assessment practices.
3. Community Engagement and Parental Involvement
Engaging families as partners in children's learning journey promotes a supportive home environment and strengthens the connection between home and school. Parent education workshops, family literacy programs, and community outreach initiatives foster collaboration and mutual support.
4. Investment in Infrastructure and Resources
Building and renovating ECE centers, equipping them with age-appropriate learning materials, and ensuring access to essential services are essential steps toward improving learning environments and enhancing educational outcomes.
5. Research and Data-driven Decision-making
Conducting research on effective ECE practices, monitoring program impact, and using data to inform decision-making promotes evidence-based interventions and continuous quality improvement in early childhood education.